Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory condition affecting an estimated 450,000 people in the United States. As reported by the American Gastroenterological Association, EoE is rapidly increasing in both incidence and prevalence, posing significant challenges for patients and healthcare systems alike. This inflammatory disorder causes white blood cells to accumulate in the esophagus, leading to symptoms like pain and difficulty swallowing that can severely impact quality of life. As if dealing with a rebellious esophagus wasn’t enough, EoE often brings along its sidekick: mental health issues, creating a two-for-one deal nobody asked for. It’s as if EoE is vying for the “Most Complicated Digestive Disorder” award, and frankly, it’s doing a stellar job.
Mental Health Challenges
Mental health challenges are a significant concern for individuals living with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Studies have shown that both adult and pediatric patients with EoE are at risk for anxiety and depression symptoms, stemming from the disease process itself and its impact on daily life. A 2019 study found that 31% of adult EoE patients had at least one psychiatric or neuropsychiatric comorbidity, with 12% diagnosed with depression and 9.3% with anxiety. These rates were significantly higher than in the general hospital population. Additionally, illness stigma has been associated with increased anxiety and depression symptoms in EoE patients, even when controlling for disease severity and duration.
Healthcare System Burden
The economic impact of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) on the healthcare system is substantial. A study examining healthcare utilization and costs found that EoE patients incurred significantly higher annual healthcare expenses compared to matched controls, with mean annual costs reaching $3,304 for pediatric patients and $5,908 for adult patients. These increased costs are attributed to:
* More frequent outpatient visits and endoscopic procedures
* Higher rates of emergency department visits and hospitalizations
* Increased medication use, including proton pump inhibitors and topical steroids
* Additional expenses related to dietary modifications and nutritional supplements
The growing prevalence of EoE, coupled with its chronic nature and need for ongoing management, suggests that the economic burden on healthcare systems will continue to rise in the coming years.
Help May Be On The Way From Eupraxia!

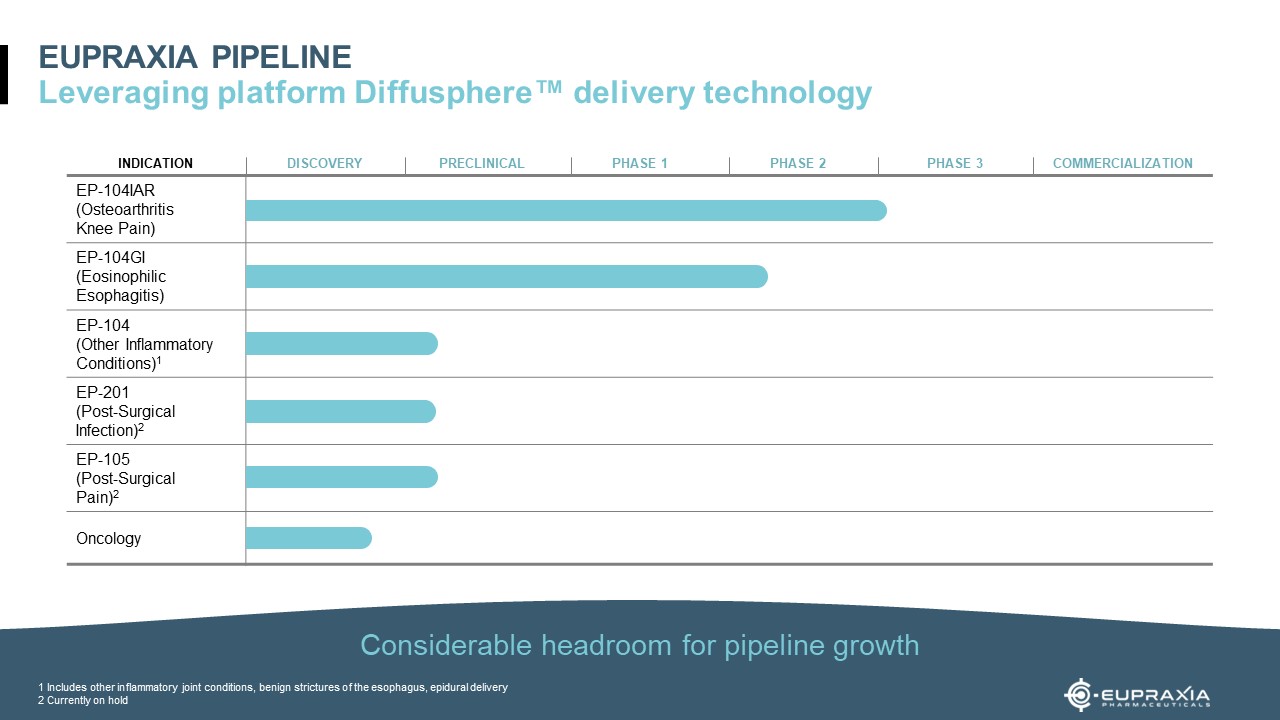
Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals Inc. (NASDAQ: EPRX), a clinical-stage biotechnology company leveraging its proprietary DiffuSphere™ technology to optimize drug delivery for applications with significant unmet need, announced on September 11, additional positive clinical data from its RESOLVE Phase 1b/2a trial, which is evaluating the safety and efficacy of EP-104GI as a treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis (“EoE”). The RESOLVE trial is a Phase 1b/2a, multicentre, open-label, dose-escalation study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of EP-104GI in adults with histologically confirmed, active EoE. EP-104GI is administered as a single dose via 4 to 20 injections into the esophageal wall. Dose escalations increase the dose per site and/or number of sites. Participants in the first fourth cohorts will be assessed for up to 24 weeks. Patients in cohorts five and above will be assessed for 52 weeks.
The results announced from the fourth cohort of the RESOLVE trial, using Eupraxia’s DiffuSphere™ technology for EoE, are derived from twelve 2.5 mg injections of EP-104GI (total dose of 30 mg) administered to less than two-thirds of each patient’s lower esophagus. The data show:
-
Straumann Dysphagia Index (“SDI”)1, a patient-reported outcome measure designed to assess symptom severity, was lower for all three patients post-administration with peak reductions up to four points (67% from baseline). At 12 weeks post-administration, SDI was reduced by a mean of 45% or 3.3 points – a level comparable with currently approved therapies.
-
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histology Scoring System (“EoEHSS”)2 scores, which evaluate the severity and extent of EoE, showed the largest percent reduction of any cohort to date, with a mean 39% reduction in Composite Stage and a mean 37% reduction in Composite Grade at 12 weeks – a level comparable with currently approved therapies.
-
Using data from four biopsy sites, which is consistent with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) Guidance for Developing Drugs for the Treatment of EoE, the mean reduction in Peak Eosinophil Counts (“PEC”)3 was 67% at 12 weeks.

Dr. James Helliwell, CEO of Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals (NASDAQ: EPRX)
“The RESOLVE trial is progressing rapidly and we continue to observe positive data on efficacy and safety outcomes with EP-104GI, with the fifth cohort expected to read out in November 2024. Overall, we are encouraged by the data that we have seen across a number of key metrics and remain optimistic that we’ll see further improvements in patient response as the trial progresses towards an optimal dosing level. In each of the trial’s successive cohorts, patients are injected with EP-104GI at either higher doses or across a greater number of injection sites. We anticipate that the dose-escalating cohorts will allow us to evaluate the trial’s emerging dose-response relationship. In addition, biopsies measuring tissue health have demonstrated a correlation between the dose of drug and the response on histology. This is exactly the outcome we hope to see in a dose-escalation trial such as this,” stated Dr. James Helliwell, Chief Executive Officer of Eupraxia.
Notes
|
1. |
Straumann Dysphagia Index, or SDI, is a patient-reported outcome score that uses a seven-day recall measuring dysphagia (trouble swallowing) severity and frequency. A reduction in SDI is a positive outcome for the RESOLVE trial. |
|
2. |
In the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histology Scoring System, or EoEHSS, grade indicates the severity of each of the eight histologic features assessed by the EoEHSS while stage indicates their extent. For the RESOLVE trial, these features include inflammation, increased cell production in a normal tissue or organ, and fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, and five other features. A reduction in EoEHSS is a positive outcome for the RESOLVE trial. |
|
3. |
Peak Eosinophil Counts, or PEC, means the peak number of eosinophils found in esophageal biopsies. Eosinophils are one of several white blood cells that support a person’s immune system. A reduction in PEC is a positive outcome for the RESOLVE trial. |

Dr. Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH
“I’m encouraged to see the positive trends in the SDI1, EoEHSS2 and PEC3 scores as the trial continues. These metrics have emerged as key data points to help clinicians better understand a patient’s esophageal health and will be important in informing the design of the Company’s late-stage clinical trials. We believe that EP-104GI has the potential to contribute to improved overall esophageal health in patients, in part, because it is being injected into the deeper areas of the esophagus versus coating the surface of the tissues, which may help to improve esophageal remodeling,”stated Dr. Evan S. Dellon, MD, MPH (University of North Carolina School of Medicine) and Chairman of the Company’s Gastrointestinal Clinical Advisory Board
Exploring Eupraxia’s DiffuSphere™ Technology
Many drugs have the potential to work well but are limited by the way they are delivered. This can lead to unwanted side effects, poor efficacy and a short duration of action. Eupraxia’s polymer-based proprietary Diffusphere™ technology aims to provide better therapy by delivering the right dose of drug, in the right place and for the right amount of time.
Traditional polymer-based approaches mix a relatively large amount of polymer with a tiny amount of drug. The drug is released as the polymer dissolves and exposes the drug particles, which can lead to variability in the drug release. This unpredictability of drug release can translate into unwanted side effects and poor results. Moreover, the large amount of polymer can also cause additional side effects as it degrades. In contrast, Eurpaxia coats the drug with a micro-thin polymer membrane that is designed to release drug at a pre-defined rate. As the inner drug core dissolves, it creates a saturated solution inside the membrane. The polymer membrane is designed to release drug at a constant rate until the drug is gone. By using less polymer and extending the time the drug remains in the most effective concentration range, Eupraxia’s technology aims to offer the dual potential of longer-lasting therapy and fewer side effects.Their manufacturing method offers several ways to fine-tune the drug release profile, making it potentially suitable for a wide range of drugs that may be improved by locally targeted and extended-release.
On July 9, a Tribe Public CEO Presentation and Q&A Webinar Event titled “Exploring The Rapid Rise Of Osteoarthritis” was held with James A. Helliwell, MD, Director and Chief Executive Officer of Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals (NASDAQ: EPRX). Please view the event video below: